Παρένθεση: Gomi, επειδή την ψάχνεις με την υποξία, βλέπω ότι ο VEGF, η απουσία του οποίου προκαλεί υποξία, αλληλορυθμίζεται με τις προσταγλανδίνες. Η αύξηση του VEGF μπορεί να δημιουργήσει hair growth, η απουσία του τριχόπτωση. Η σχέση του με τις προσταγλανδίνες είναι το best part που επιβεβαιώνει την έρευνα του Κοτσαρέλη: Pgf2a και Pge διεγείρουν τον VEGF, αντιθέτως ο Pgd2 τον καταστέλλει. Τι είπε ο Κοτσαρέλης ότι βρήκε στα φαλακρά κεφάλια σε μεγάλες ποσότητες είπαμε;
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Η διατροφή του accutane, της φιναστερίδης και της μινοξιδίλης
- Έναρξη μίζας GOMI
- Ημερομηνία έναρξης
Παρακαλώ συνδεθείτε ή εγγραφείτε για να απενεργοποιήσετε τις διαφημίσεις.
pazuzu είπε:Παρένθεση: Gomi, επειδή την ψάχνεις με την υποξία, βλέπω ότι ο VEGF, η απουσία του οποίου προκαλεί υποξία, αλληλορυθμίζεται με τις προσταγλανδίνες. Η αύξηση του VEGF μπορεί να δημιουργήσει hair growth, η απουσία του τριχόπτωση. Η σχέση του με τις προσταγλανδίνες είναι το best part που επιβεβαιώνει την έρευνα του Κοτσαρέλη: Pgf2a και Pge διεγείρουν τον VEGF, αντιθέτως ο Pgd2 τον καταστέλλει. Τι είπε ο Κοτσαρέλης ότι βρήκε στα φαλακρά κεφάλια σε μεγάλες ποσότητες είπαμε;
φίλε pazuzu, νομίζω ότι βρήκα την αιτία που συμβάλει στη δική μου Α.Α. Όταν συνέλθω λίγο ψυχολογικά και έχω όρεξη, ίσως αποπειραθώ να το εξηγήσω
weznem
Well-Known Member
Atermon είπε:Μιας και μιλούσαμε για χαμηλό ψευδάργυρο σε άτομα με ΑΑ, έχετε παρατηρήσει ασπραδάκια στα νύχια σας, όπως λέγεται ότι αυτό είναι ένδειξη έλλειψης ψευδαργύρου;
εγω ξερω οτι αυτο που λες σχετιζεται με την μπανανα οποτε μη[ως ειναι καλιο η μαγνησιο?
Atermon είπε:Μιας και μιλούσαμε για χαμηλό ψευδάργυρο σε άτομα με ΑΑ, έχετε παρατηρήσει ασπραδάκια στα νύχια σας, όπως λέγεται ότι αυτό είναι ένδειξη έλλειψης ψευδαργύρου;
Μπορεί να είναι και από έλλειψη ασβεστίου. Γενικότερα όμως, αν η αιτία είναι από έλλειψη ψευδαργύρου πχ. αφορά περισσότερο σε χαμηλά επίπεδα του και όχι τόσο μέσα στα φυσιολογικά χαμηλά όρια.
Komis
Active Member
Γιατι σε οσους εχουν καρκινο στο προστατη προσπαθουνε να μειωσουνε την πρωτεινη vegf?
Gomi,το εψαξα αλλα δεν καταφερα να βγαλω ακρη για αυτο σε ρωταω...
Γνωριζεις αν το γανοδερμα προκαλει μειωση της vegf?
Στα καρκινικα κυτταρα,αν καταλαβα καλα,το γανοδερμα προκαλει μειωση του vegf,οπως και του TGF-b.
Κανει το ιδιο και στο κεφαλι?
Gomi,το εψαξα αλλα δεν καταφερα να βγαλω ακρη για αυτο σε ρωταω...
Γνωριζεις αν το γανοδερμα προκαλει μειωση της vegf?
Στα καρκινικα κυτταρα,αν καταλαβα καλα,το γανοδερμα προκαλει μειωση του vegf,οπως και του TGF-b.
Κανει το ιδιο και στο κεφαλι?
Komis είπε:Γιατι σε οσους εχουν καρκινο στο προστατη προσπαθουνε να μειωσουνε την πρωτεινη vegf?
Gomi,το εψαξα αλλα δεν καταφερα να βγαλω ακρη για αυτο σε ρωταω...
Γνωριζεις αν το γανοδερμα προκαλει μειωση της vegf?
Στα καρκινικα κυτταρα,αν καταλαβα καλα,το γανοδερμα προκαλει μειωση του vegf,οπως και του TGF-b.
Κανει το ιδιο και στο κεφαλι?
Θεωρητικά, ότι απορροφάται, λίγο πολύ έχει τις ίδιες ιδιότητες που έχει και όραλ. Απλά συνήθως σε μικρότερο βαθμό.
Ναι, από τις έρευνες το γανόδερμα φαίνεται να έχει αντιαγγειογενετικές ιδιότητες γι αυτό και όσα έχουν αντικαρκινικές ιδιότητες, συνήθως αφορούν την εμπόδιση της αγγειογένεσης ώστε να αποφευχθεί όσο το δυνατόν η εξάπλωση.
Αυτό όμως που τρέφει τους καρκινικούς όγκους, είναι η αγγειογένεση που προκαλείται μέσω της μεταλλοπρωτεϊνάσης mmp-9.
Κάτι αντίστοιχο ανέφερα εδώ στον kapa
http://www.hairlossgr.com/forum/thread-9126-page-4.html
To γανόδερμα έχει πολύ καλή δράση σε αυτόν τον παράγοντα.
Δες εδώ
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21028821
Τοπικό με αντίστοιχες ιδιότητες χρησιμοποιώ και εγώ. Μια τέτοιου είδους αγγειογένεση, κάτι που φαίνεται ότι είναι δεδομένο στην Α.Α. δεν την θέλουμε, γιατί είναι ο δρόμος που ανοίγεται για τα μακροφάγα κύτταρα προκαλώντας ταυτόχρονα αλλοίωση της σύστασης του κολλαγόνου.
Komis
Active Member
Oποτε αν καταλαβα καλα, δεν θελουμε την αυξηση του vegf οπως εχει αναφερθει εδω μεσα.
Το να εμποδιζεις την αγγειογενεση στο τριχωτο της κεφαλης δεν ειναι αρνητικο?
Αγγειογενεση δεν σημαινει δημιουργεια νεων αγγειων αρα και καλυτερη κυκλοφορια με περισσοτερο αιμα στον θυλακα?
Ισως σε καρκινικα κυτταρα η αναστολη της αγγειογενεσης να δουλευει θετικα.Εμεις ομως θελουμε το αντιθετο..
Τα ειχα διαβασει περι παρεμποδισης της αγγειογενεσης αλλα ειχα κολλησει στα σημεια που προανεφερα.
Το να εμποδιζεις την αγγειογενεση στο τριχωτο της κεφαλης δεν ειναι αρνητικο?
Αγγειογενεση δεν σημαινει δημιουργεια νεων αγγειων αρα και καλυτερη κυκλοφορια με περισσοτερο αιμα στον θυλακα?
Ισως σε καρκινικα κυτταρα η αναστολη της αγγειογενεσης να δουλευει θετικα.Εμεις ομως θελουμε το αντιθετο..
Τα ειχα διαβασει περι παρεμποδισης της αγγειογενεσης αλλα ειχα κολλησει στα σημεια που προανεφερα.
οι mmp-9 είναι παράγοντες του vegf. Μπορεί να υπάρξει αγγειογένεση και χωρίς αυτές και η οποία είναι η φυσιολογική αγγειογένεση που εξυπηρετεί συγκεκριμένους σκοπούς.
Αγγειογένεση μέσω mmp-9 αφορά καθαρά συντήρηση - επιδείνωση της φλεγμονής και έχει να κάνει με την δράση του ανοσοποιητικού.
Δεν με ανησυχεί τόσο το ότι μπλοκάρουμε κατά κάποιο τρόπο αυτή την αγγειογένεση, γιατί για τα μαλλιά είναι ευεργετικό. Το θέμα είναι τι προσπαθεί να καταπολεμήσει το ανοσοποιητικό και εμείς το εμποδίζουμε...
Αγγειογένεση μέσω mmp-9 αφορά καθαρά συντήρηση - επιδείνωση της φλεγμονής και έχει να κάνει με την δράση του ανοσοποιητικού.
Δεν με ανησυχεί τόσο το ότι μπλοκάρουμε κατά κάποιο τρόπο αυτή την αγγειογένεση, γιατί για τα μαλλιά είναι ευεργετικό. Το θέμα είναι τι προσπαθεί να καταπολεμήσει το ανοσοποιητικό και εμείς το εμποδίζουμε...
Exogenous Testosterone, Finasteride and Castration Effects on Testosterone, Insulin, Zinc and Chromium in Adult Male Rats
όλη η έρευνα εδώ
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3600969/
In conclusion, the study demonstrates that testosterone and finasteride increases insulin and zinc levels and decreases chromium levels in the serum of male adult rats. These data also suggest that testosterone affects glucose cycle through effect on serum levels of insulin and trace elements such as zinc and chromium.
όλη η έρευνα εδώ
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3600969/
In conclusion, the study demonstrates that testosterone and finasteride increases insulin and zinc levels and decreases chromium levels in the serum of male adult rats. These data also suggest that testosterone affects glucose cycle through effect on serum levels of insulin and trace elements such as zinc and chromium.
Hyperinsulinemic diseases of civilization: more than just Syndrome X.
Cordain L, Eades MR, Eades MD.
Author information
Abstract
Compensatory hyperinsulinemia stemming from peripheral insulin resistance is a well-recognized metabolic disturbance that is at the root cause of diseases and maladies of Syndrome X (hypertension, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, coronary artery disease, obesity, abnormal glucose tolerance).
Abnormalities of fibrinolysis and hyperuricemia also appear to be members of the cluster of illnesses comprising Syndrome X.
Insulin is a well-established growth-promoting hormone, and recent evidence indicates that hyperinsulinemia causes a shift in a number of endocrine pathways that may favor unregulated tissue growth leading to additional illnesses.
Specifically, hyperinsulinemia elevates serum concentrations of free insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and androgens, while simultaneously reducing insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG).
Since IGFBP-3 is a ligand for the nuclear retinoid X receptor alpha, insulin-mediated reductions in IGFBP-3 may also influence transcription of anti-proliferative genes normally activated by the body's endogenous retinoids.
These endocrine shifts alter cellular proliferation and growth in a variety of tissues, the clinical course of which may promote acne, early menarche, certain epithelial cell carcinomas, increased stature, myopia, cutaneous papillomas (skin tags), acanthosis nigricans, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and male vertex balding. Consequently, these illnesses and conditions may, in part, have hyperinsulinemia at their root cause and therefore should be classified among the diseases of Syndrome X.
Cordain L, Eades MR, Eades MD.
Author information
Abstract
Compensatory hyperinsulinemia stemming from peripheral insulin resistance is a well-recognized metabolic disturbance that is at the root cause of diseases and maladies of Syndrome X (hypertension, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, coronary artery disease, obesity, abnormal glucose tolerance).
Abnormalities of fibrinolysis and hyperuricemia also appear to be members of the cluster of illnesses comprising Syndrome X.
Insulin is a well-established growth-promoting hormone, and recent evidence indicates that hyperinsulinemia causes a shift in a number of endocrine pathways that may favor unregulated tissue growth leading to additional illnesses.
Specifically, hyperinsulinemia elevates serum concentrations of free insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and androgens, while simultaneously reducing insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG).
Since IGFBP-3 is a ligand for the nuclear retinoid X receptor alpha, insulin-mediated reductions in IGFBP-3 may also influence transcription of anti-proliferative genes normally activated by the body's endogenous retinoids.
These endocrine shifts alter cellular proliferation and growth in a variety of tissues, the clinical course of which may promote acne, early menarche, certain epithelial cell carcinomas, increased stature, myopia, cutaneous papillomas (skin tags), acanthosis nigricans, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and male vertex balding. Consequently, these illnesses and conditions may, in part, have hyperinsulinemia at their root cause and therefore should be classified among the diseases of Syndrome X.
Παρακαλώ συνδεθείτε ή εγγραφείτε για να απενεργοποιήσετε τις διαφημίσεις.
Μια πάρα πολύ ενδιαφέρουσα και εμπεριστατωμένη έρευνα, που αφορά τη σύγκριση γυναικών δίχως και με πολυκυστικές ωοθήκες.
http://www.ptantropologiczne.pl/en/ckfinder/userfiles/images/AR/vol76_2/AR_76-2_183-198.pdf
Στον πρώτο πίνακα της έρευνας, φαίνεται καθαρά η σύγκριση των συμμετεχόντων σε βασικές τιμές εξετάσεων.
Οι γυναίκες με πολυκυστικές, είχαν αρκετά αυξημένο δείκτη ελεύθερων ανδρογόνων
FAI 4.07 ± 2.85 --------- 1.42 ± 0.71
Χαμηλότερη shbg
SHBG, nmol/l 62.34 ± 30.17 -----------75.84 ± 22.15
χαμηλότερη καλή χοληστερίνη
HDL cholesterol, mmol/l 1.72 ± 0.31 -----------1.85 ± 0.30
αυξημένη κακή χοληστερίνη
LDL cholesterol, mmol/l 2.67 ± 0.79 ----------- 2.51 ± 0.70
Υψηλότερα τριγλυκερίδια
TG, mmol/l 0.88 ± 0.40 ---------- 0.75 ± 0.33
Αυξημένη γλυκόζη
Glucose, mmol/l 4.94 ± 0.41 ---------- 4.75 ± 0.48
Αυξημένη ινσουλίνη αίματος
Insulin, µU/ml 7.35 ± 4.34 ----------6.20 ± 2.85
αυξημένη αντίσταση στην ινσουλίνη homeostasis model of assessment-insulin resistance
HOMA-IR 1.64 ± 1.05 -------- 1.32 ± 0.65
Body composition parameters, comprising estimated skeletal mass, skin
and subcutaneous adipose tissue mass,
muscle mass and relative and absolute passive mass in PCOS women, differed to control values (p<0.05) (Table 2)
Lean PCOS women had slightly greater
mean skeletal mass by 0.47 kg (p<0.05,
Cohen’s d=1.14), greater mean skin
and subcutaneous adipose tissue mass
by 2.79 kg (p<0.05, Cohen’s d=6.07)
and lower mean muscle mass by 1.47
kg (p<0.05, Cohen’s d=2.84) compared
to controls (p<0.05).
The mean somatotypes for each
group were compared and found to be
significantly different (p=0.031) due to
endomorphic difference (p=0.002).
Conclusion
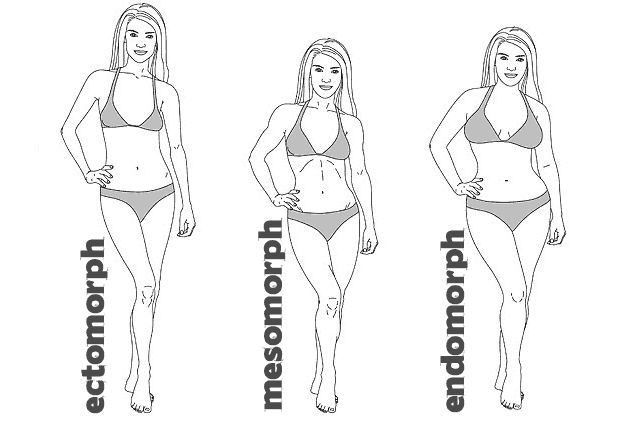
Lean women with polycystic ovary syndrome had a mesomorphic endomorph-somatotype and higher skin and subcutaneous adipose tissue mass, but less muscle mass than lean healthy women.
Here, skin and subcutaneous adipose tissue positively correlated with insulin and HOMA-IR in our lean PCOS women
Περισσότερο το αναφέρω γιατί συχνά πυκνά οι pcos έχουν συσχετιστεί άμεσα με την Α.Α. σε πολλά σημεία και αυτό που φαίνεται ότι παίζει σοβαρό ρόλο στην όλη διαδικασία αντίστασης στην ινσουλίνη και αύξηση των ελεύθερων ανδρογόνων είναι ο σωματότυπος του καθενός.
Ίσως τελικά, πάνω κάτω, αυτό να κληρονομούμε...τον σωματότυπο που θα κρίνει στην πορεία πως θα διαχειρίζεται ο οργανισμός μας την ομοιόσταση.

http://www.ptantropologiczne.pl/en/ckfinder/userfiles/images/AR/vol76_2/AR_76-2_183-198.pdf
Στον πρώτο πίνακα της έρευνας, φαίνεται καθαρά η σύγκριση των συμμετεχόντων σε βασικές τιμές εξετάσεων.
Οι γυναίκες με πολυκυστικές, είχαν αρκετά αυξημένο δείκτη ελεύθερων ανδρογόνων
FAI 4.07 ± 2.85 --------- 1.42 ± 0.71
Χαμηλότερη shbg
SHBG, nmol/l 62.34 ± 30.17 -----------75.84 ± 22.15
χαμηλότερη καλή χοληστερίνη
HDL cholesterol, mmol/l 1.72 ± 0.31 -----------1.85 ± 0.30
αυξημένη κακή χοληστερίνη
LDL cholesterol, mmol/l 2.67 ± 0.79 ----------- 2.51 ± 0.70
Υψηλότερα τριγλυκερίδια
TG, mmol/l 0.88 ± 0.40 ---------- 0.75 ± 0.33
Αυξημένη γλυκόζη
Glucose, mmol/l 4.94 ± 0.41 ---------- 4.75 ± 0.48
Αυξημένη ινσουλίνη αίματος
Insulin, µU/ml 7.35 ± 4.34 ----------6.20 ± 2.85
αυξημένη αντίσταση στην ινσουλίνη homeostasis model of assessment-insulin resistance
HOMA-IR 1.64 ± 1.05 -------- 1.32 ± 0.65
Body composition parameters, comprising estimated skeletal mass, skin
and subcutaneous adipose tissue mass,
muscle mass and relative and absolute passive mass in PCOS women, differed to control values (p<0.05) (Table 2)
Lean PCOS women had slightly greater
mean skeletal mass by 0.47 kg (p<0.05,
Cohen’s d=1.14), greater mean skin
and subcutaneous adipose tissue mass
by 2.79 kg (p<0.05, Cohen’s d=6.07)
and lower mean muscle mass by 1.47
kg (p<0.05, Cohen’s d=2.84) compared
to controls (p<0.05).
The mean somatotypes for each
group were compared and found to be
significantly different (p=0.031) due to
endomorphic difference (p=0.002).
Conclusion
Lean women with polycystic ovary syndrome had a mesomorphic endomorph-somatotype and higher skin and subcutaneous adipose tissue mass, but less muscle mass than lean healthy women.
Here, skin and subcutaneous adipose tissue positively correlated with insulin and HOMA-IR in our lean PCOS women
Περισσότερο το αναφέρω γιατί συχνά πυκνά οι pcos έχουν συσχετιστεί άμεσα με την Α.Α. σε πολλά σημεία και αυτό που φαίνεται ότι παίζει σοβαρό ρόλο στην όλη διαδικασία αντίστασης στην ινσουλίνη και αύξηση των ελεύθερων ανδρογόνων είναι ο σωματότυπος του καθενός.
Ίσως τελικά, πάνω κάτω, αυτό να κληρονομούμε...τον σωματότυπο που θα κρίνει στην πορεία πως θα διαχειρίζεται ο οργανισμός μας την ομοιόσταση.


gianniskritikos2
Active Member
gomi ο σωματοτυπος νομιζεις εχει σχεση??? γιατι εγω δεν νομιζω... εγω ειμαι εκτομορφικος και ο πατερας μου μεσομορφικος αλλα πλεων ειναι ενδο.. εχει παχυνει...
Ανεξαρτήτως αν κάποιος τρώει φυσιολογικά ή σαν μοσχάρι, φαίνεται ότι ο σωματότυπος, παίζει ρόλο στο πως διαχειρίζεται το σώμα την ινσουλίνη. Οι καθαρά εκτομορφικοί, ίσως είναι οι πιο τυχεροί σε αυτόν τον τομέα και οι άτυχοι της υπόθεσης, όσοι το σώμα τους συνδυάζει 2 χαρακτηριστικά, όπως πχ στην παραπάνω έρευνα που αφορά τους μεσοενδομορφικούς.
Σωματότυπο απ όσα διάβασα, δεν μπορούμε να αλλάξουμε πριν τα 50 - 60, άσχετα αν η διατροφή μας αλλάζει τα εξωτερικά χαρακτηριστικά.
Εγώ πάλι είμαι καθαρά μεσοενδομορφικός...αν αφεθώ, πάω καθαρά για ενδομορφικό βουβαλάκι...
Σωματότυπο απ όσα διάβασα, δεν μπορούμε να αλλάξουμε πριν τα 50 - 60, άσχετα αν η διατροφή μας αλλάζει τα εξωτερικά χαρακτηριστικά.
Εγώ πάλι είμαι καθαρά μεσοενδομορφικός...αν αφεθώ, πάω καθαρά για ενδομορφικό βουβαλάκι...
gianniskritikos2
Active Member
ειμαι τερμα εκτομορφικος 100% τροω μακαρονια 1 η ωρα το βραδι και δεν βαζω γραμμαριο... δεν εχω ανεβει ποτε πανο απο 10% λιπος ποτε... ειμαι παντα ινες πριν κανα 5 μηνο που δεν προσεχα διατροφη ετρογα οτι γουσταρα 5 σουβλακια 2 πιτσες μονος... τροω απιστεφτες ποσοτιτες που με κοροιδευει ολη η οικογενια μου λενε που τα χωραω.... απο οτι καταλαβαινεις ειμαι εκτομορφικος τερμα ομως.... και ομως καραφλιαζω... αρα η η ινσουλινη δεν πεζει κανενα ρολο στην καραφλα αρα τσαμπα δεν τροω γαλακτοκυκα... η δεν ξερω...
gianniskritikos2 είπε:ειμαι τερμα εκτομορφικος 100% τροω μακαρονια 1 η ωρα το βραδι και δεν βαζω γραμμαριο... δεν εχω ανεβει ποτε πανο απο 10% λιπος ποτε... ειμαι παντα ινες πριν κανα 5 μηνο που δεν προσεχα διατροφη ετρογα οτι γουσταρα 5 σουβλακια 2 πιτσες μονος... τροω απιστεφτες ποσοτιτες που με κοροιδευει ολη η οικογενια μου λενε που τα χωραω.... απο οτι καταλαβαινεις ειμαι εκτομορφικος τερμα ομως.... και ομως καραφλιαζω... αρα η η ινσουλινη δεν πεζει κανενα ρολο στην καραφλα αρα τσαμπα δεν τροω γαλακτοκυκα... η δεν ξερω...
Ναι, μπορεί και να μην παίζει, ή μπορεί να παίζει ρόλο μέχρι ενός σημείου. Τπτ δεν είναι αποδεδειγμένο, αλλά λίγο πολύ αυτό ισχύει για όλα. Ακόμα για για την dht. Ποιός έχει αποδείξει πέραν από πάσα αμφιβολία για το τι φταίει? Κανείς..
Από την άλλη όμως, εδώ μιλάμε για φυσιολογικό διαχειρισμό της ινσουλίνης από το σώμα. Αν τώρα για παράδειγμα, εσύ όπως αναφέρεις τρως τεράστιες ποσότητες, όσο να ναι, κάπου θα ξεφεύγεις σε τιμές.
Στην παλιά μου γειτονιά, είχα ένα φίλο που μεγαλώσαμε από μικροί μαζί. Αυτός ήταν αδύνατος και έτρωγε ακριβώς όπως εσύ και όλοι στην παρέα τον ζηλεύαμε γτ δεν έπαιρνε γραμμάριο.
Από 24χρ. παντρεύτηκε και έφυγε από τη γειτονιά (πάνε αρκετά χρόνια δηλαδή) και τον είδα πριν περίπου 2 χρόνια στο δρόμο και τα λέγαμε.
Ήταν nw6 και με αρκετά κιλά πάνω του με το σύνολο αυτών στην κοιλιά...
Γνωρίζοντάς τον από μικρό, θα έλεγα ότι ήταν καθαρά εκτόμορφος. Βλέποντάς όμως τώρα, θα έλεγα ότι είναι καθαρά ενδόμορφος...
Παρόλο αυτά, παίζει δεν παίζει ρόλο, (εγώ πιστεύω βέβαια πως παίζει, αλλά δεν ξέρω πόσο) δεν έχει και τόσο νόημα να το ψάχνουμε, γτ δεν μπορούμε να κάνουμε τπτ...
A critical defect in type 2 diabetes is impaired insulin-stimulated glucose transport and metabolism in muscle and adipocytes. To understand the metabolic adaptations this elicits, we generated mice with targeted disruption of the GLUT4 glucose transporter in both adipocytes and muscle (AMG4KO)
They develop fasting hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance and are at risk for greater insulin resistance than mice lacking GLUT4
GLUT4, the major insulin-regulated glucose transporter, is expressed primarily in skeletal and cardiac muscle and adipocytes, with low-level expression in a few other tissues (10, 11). GLUT4 expression is downregulated in adipocytes, while GLUT4 function is impaired in skeletal muscle in most type 2 diabetic patients (2). Adipose tissue is an important endocrine organ, but it utilizes relatively little glucose compared with muscle.
Mice in which GLUT4 has been reduced in either tissue have glucose intolerance and insulin resistance.
http://www.jci.org/articles/view/21341
The aim of this study was to determine if the previously described insulin resistance in the New Zealand Obese (NZO) mouse is associated with a decrease in GLUT4 protein and if such changes occur early in the evolution of the syndrome.
GLUT4 levels were measured in whole membranes isolated from a variety of tissues in 4 and 20-week-old NZO and control NZC mice by Western blotting using a specific antibody to the C terminal end of the protein.
At 20 weeks of age, GLUT4 levels were lower in the NZO mice in brown and white adipose tissue, heart, diaphragm, red and white quadriceps, and red and white gastrocnemius, but not in soleus muscle. At 4 weeks of age, GLUT4 levels were 52% lower in BAT (3309 +/- 1006 vs 6951 +/- 1870 cpm P = 0.039) but were not lower in WAT, heart or red quadriceps. It is concluded that adult NZO mice have a decrease in GLUT4 levels in most insulin-sensitive tissues and that in BAT, this occurs at an early age.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7866477
Here, we investigated the effect of a zinc-chelated vitamin C (ZnC) compound on the adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Treatment with ZnC for 8 d significantly promoted adipogenesis, which was characterized by increased glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and intracellular lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells.
Meanwhile, ZnC induced a pronounced up-regulation of the expression of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) and the adipocyte-specific gene adipocyte protein 2 (aP2).
These results indicate that ZnC could promote adipogenesis through PPARγ and C/EBPα, which act synergistically for the expression of aP2 and GLUT4, leading to the generation of insulin-responsive adipocytes and can thereby be useful as a novel therapeutic agent for the management of diabetes and related metabolic disorders.
CONCLUSION
In the present study, we demonstrated that ZnC significantly promoted the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by enhancing the expression of the key transcription factors C/EBPα and PPARγ and the related adipogenic target gene aP2.
Moreover, ZnC also stimulated the expression of GLUT4, a key regulator of insulin-mediated glucose transport in adipocytes. Taken together, these findings are helpful in understanding the insulin sensitizing and adipogenic properties of ZnC, which can be used as a novel therapeutic agent for the management of diabetes and related metabolic disorders. However, further studies are needed to assess the specific mechanism underlying the observed effects of ZnC.
http://www.e-sciencecentral.org/articles/SC000000172
Από τις έρευνες αυτές φαίνεται ότι το γονίδιο glut4 που βρίσκεται στο μυικό ιστό αλλά και στον λιπώδη ιστό, όταν μειώνεται οδηγεί αυτούς τους ιστούς να αναπτύξουν αντίσταση στην ινσουλίνη μιας και αυτό είναι ο μεταφορέας της γλυκόζης στα κύτταρα.
Από την άλλη, φαίνεται ότι μια συγκεκριμένη μορφή ψευδαργύρου εκτός του ότι αυξάνει αυτό το γονίδιο προκαλεί και λιπογένεση δημιουργώντας λιποκύτταρα τα οποία έχουν αυξημένη ευαισθησία στην ινσουλίνη.
Προφανώς για οραλ χρήση μοιάζει πολύ καλό, ΣΥΜΦΩΝΑ ΜΕ ΟΣΑ ΑΝΑΦΕΡΕΙ Η ΕΡΕΥΝΑ, αλλά αναρωτιέμαι κατά πόσο θα μπορούσε να ήταν εξίσου ενδιαφέρον για τοπική εφαρμογή με το σκεπτικό ότι αν καταφέρει να αυξήσει την λιπογένεση που αποδεδειγμένα είναι μειωμένη στα φαλακρά κεφάλια, ταυτόχρονα θα βοηθήσει και τα κύτταρα να ανταποκριθούν στην ινσουλίνη, αποθηκεύοντας στον πυρήνα τους γλυκόζη.:chinscratch
Μορφές αυτού του ψευδαργύρου μέχρι στιγμής έχω βρει αυτές
http://www.iherb.com/Pharmax-Zinc-C-CWS-1-fl-oz-30-ml/52017
http://www.ebay.com/sch/i.html?_trksid=p2053587.m570.l1313&_nkw=ZINC+ASCORBATE&_sacat=0&_from=R40
They develop fasting hyperglycemia and glucose intolerance and are at risk for greater insulin resistance than mice lacking GLUT4
GLUT4, the major insulin-regulated glucose transporter, is expressed primarily in skeletal and cardiac muscle and adipocytes, with low-level expression in a few other tissues (10, 11). GLUT4 expression is downregulated in adipocytes, while GLUT4 function is impaired in skeletal muscle in most type 2 diabetic patients (2). Adipose tissue is an important endocrine organ, but it utilizes relatively little glucose compared with muscle.
Mice in which GLUT4 has been reduced in either tissue have glucose intolerance and insulin resistance.
http://www.jci.org/articles/view/21341
The aim of this study was to determine if the previously described insulin resistance in the New Zealand Obese (NZO) mouse is associated with a decrease in GLUT4 protein and if such changes occur early in the evolution of the syndrome.
GLUT4 levels were measured in whole membranes isolated from a variety of tissues in 4 and 20-week-old NZO and control NZC mice by Western blotting using a specific antibody to the C terminal end of the protein.
At 20 weeks of age, GLUT4 levels were lower in the NZO mice in brown and white adipose tissue, heart, diaphragm, red and white quadriceps, and red and white gastrocnemius, but not in soleus muscle. At 4 weeks of age, GLUT4 levels were 52% lower in BAT (3309 +/- 1006 vs 6951 +/- 1870 cpm P = 0.039) but were not lower in WAT, heart or red quadriceps. It is concluded that adult NZO mice have a decrease in GLUT4 levels in most insulin-sensitive tissues and that in BAT, this occurs at an early age.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7866477
Here, we investigated the effect of a zinc-chelated vitamin C (ZnC) compound on the adipogenic differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Treatment with ZnC for 8 d significantly promoted adipogenesis, which was characterized by increased glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase activity and intracellular lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 cells.
Meanwhile, ZnC induced a pronounced up-regulation of the expression of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) and the adipocyte-specific gene adipocyte protein 2 (aP2).
These results indicate that ZnC could promote adipogenesis through PPARγ and C/EBPα, which act synergistically for the expression of aP2 and GLUT4, leading to the generation of insulin-responsive adipocytes and can thereby be useful as a novel therapeutic agent for the management of diabetes and related metabolic disorders.
CONCLUSION
In the present study, we demonstrated that ZnC significantly promoted the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes by enhancing the expression of the key transcription factors C/EBPα and PPARγ and the related adipogenic target gene aP2.
Moreover, ZnC also stimulated the expression of GLUT4, a key regulator of insulin-mediated glucose transport in adipocytes. Taken together, these findings are helpful in understanding the insulin sensitizing and adipogenic properties of ZnC, which can be used as a novel therapeutic agent for the management of diabetes and related metabolic disorders. However, further studies are needed to assess the specific mechanism underlying the observed effects of ZnC.
http://www.e-sciencecentral.org/articles/SC000000172
Από τις έρευνες αυτές φαίνεται ότι το γονίδιο glut4 που βρίσκεται στο μυικό ιστό αλλά και στον λιπώδη ιστό, όταν μειώνεται οδηγεί αυτούς τους ιστούς να αναπτύξουν αντίσταση στην ινσουλίνη μιας και αυτό είναι ο μεταφορέας της γλυκόζης στα κύτταρα.
Από την άλλη, φαίνεται ότι μια συγκεκριμένη μορφή ψευδαργύρου εκτός του ότι αυξάνει αυτό το γονίδιο προκαλεί και λιπογένεση δημιουργώντας λιποκύτταρα τα οποία έχουν αυξημένη ευαισθησία στην ινσουλίνη.
Προφανώς για οραλ χρήση μοιάζει πολύ καλό, ΣΥΜΦΩΝΑ ΜΕ ΟΣΑ ΑΝΑΦΕΡΕΙ Η ΕΡΕΥΝΑ, αλλά αναρωτιέμαι κατά πόσο θα μπορούσε να ήταν εξίσου ενδιαφέρον για τοπική εφαρμογή με το σκεπτικό ότι αν καταφέρει να αυξήσει την λιπογένεση που αποδεδειγμένα είναι μειωμένη στα φαλακρά κεφάλια, ταυτόχρονα θα βοηθήσει και τα κύτταρα να ανταποκριθούν στην ινσουλίνη, αποθηκεύοντας στον πυρήνα τους γλυκόζη.:chinscratch
Μορφές αυτού του ψευδαργύρου μέχρι στιγμής έχω βρει αυτές
http://www.iherb.com/Pharmax-Zinc-C-CWS-1-fl-oz-30-ml/52017
http://www.ebay.com/sch/i.html?_trksid=p2053587.m570.l1313&_nkw=ZINC+ASCORBATE&_sacat=0&_from=R40
dk1984 είπε:Gomi θα χρησιμοποιουσες το ψευδαργυρο που ποσταρες με το δερμαρολλερ 1,5μμ ?
θα επερνες και συμπληρωματα χαλκου παραλληλα?
Παραμένει ένας ίσως αρνητικός παράγοντας που αφορά τον epidermal growth factor όσον αφορά τον ψευδάργυρο και το ρόλλερ 1,5mm.
Ο egf θεωρείται αρνητικός παράγοντας κατά την επούλωση πληγών σε περιοχή τριχοφυΐας, από τις έρευνες του Κωτσαρέλη, αλλά δεν τον έχω σε ιδιαίτερη υπόληψη στα όσα λέει.
Εγώ θα το χρησιμοποιούσα με ρολλερ 0.5 αλλά η πιο καλή μορφή ZnC είναι αυτή του iherb, όμως βάζοντάς το στην κάρτα, μου έβγαζε αυτό
At this time, due to regulations, this item is not allowed to be shipped to your region
Χαλκός δεν χρειάζεται αν μιλάμε για τοπική εφαρμογή.
